Epilepsy is one of the most common neurological diseases, with a incidence of nearly 1%. About 30%of patients will develop into drugs and epilepsy, especially patients with temporal lobe epilepsy accompanied by hippocampus. In addition, the treatment method is very limited. Two major pathological features of epilepsy in patients with temporal lobe epilepsy are the generation of neuron death and gel scars. The main composition cells of glue scars are reactive star gel cells. However, in the process of epilepsy, the function and molecular mechanism of reactive star gel cells are still unclear.
Recently, Professor Yan Chao, Executive Dean of Nanjing University's Artificial Intelligence Biomedical Technology Research Institute, and Professor Chen Dijun, School of Life Sciences of Nanjing University, and Director Liu Xiangyu of the Neurosurgery of Drum Tower Hospital Affiliated to Nanjing University Medical College. A new reactive astrocyte cell sub-group-Lipid-ACCUMULATED Reactive ASTROcyte (LARA); Lara is formed by the formation of APOE, showing unique molecules. Pathogenic and meke type; LARA has reduced the expression of adenosine A2A receptor, reducing the heavy intake of glutamic acid, thereby exacerbating the excitement of neurons and promoting the progress of epilepsy. The discovery can provide a new strategy for the treatment of drug -resistant epilepsy.

The researchers first analyzed the magnetic resonance imaging spectrum data of patients with Temporal Lobe Epilepsy (TLE), and found that the patient's presence of epilepsy is abnormal accumulation in the epilepsy side. Quality accumulation is an important pathological characteristics of TLE patients, and lipid accumulation mainly occurs in neurons and star gum cells. Further collecting a single -core RNA sequencing by collecting TLE patients with brain tissue samples, TLE patients are abnormally activated by star -shaped glue cell lipid metabolism and lipid transshipment signal pathways, and the lipoprotein APOE is significantly increased in astrocyte cells. Next, the researchers found in the epilepsy mice model that star -shaped glue cell -specific APOE knockout can effectively improve abnormal fat accumulation in star gel cells; in vitro cell experiments also show that a large amount of lipids caused by excessive excitement of neurons The APOE of the star -shaped glue cells is transferred to the star gel cells, causing its abnormal fat to accumulate. Researchers have found that these star -shaped gel cells with abnormal stacked stacked are a new group of reactive star gel cells. According to the single -core RNA sequencing data, they identified a star -shaped glue cell sub -group that expresses APOE, and characterized its transcriptional features. Researchers defined this sub -group as "the reactive star gel cells of the fat accumulation ", English is abbreviated as Lara.
In order to explore the role of LARA in epilepsy, the researchers conducted epilepsy in APOE knockout mice, and found that APOE knocking can effectively improve the symptoms of epilepsy, and also reverse the expression level of most LARA -related genes, indicating that APOE is the APOE is the APOE is The necessary conditions for formation of LARA, and LARA has the effect of promoting epilepsy. Finally, the research team also initially explored the potential molecular mechanism of LARA's epilepsy, and found that LARA played the role of epilepsy by raising the adenosine A2A receptor. The adenosine A2A receptor with adenoscopy A2AR inhibitors or specificity of low -star gel cells can improve the symptoms of epilepsy of model mice.
In summary, this study found that there is abnormal fat accumulation in the lesion area of TLE patients, defining a new reactive star gel cell subtype -LARA, and systematically studied LARA's molecular phenotype and function in TLE in TLE The phenotype, at the same time, revealed the role of APOE in the progress of epilepsy, provided a new strategy for the treatment of drug -resistant epilepsy.
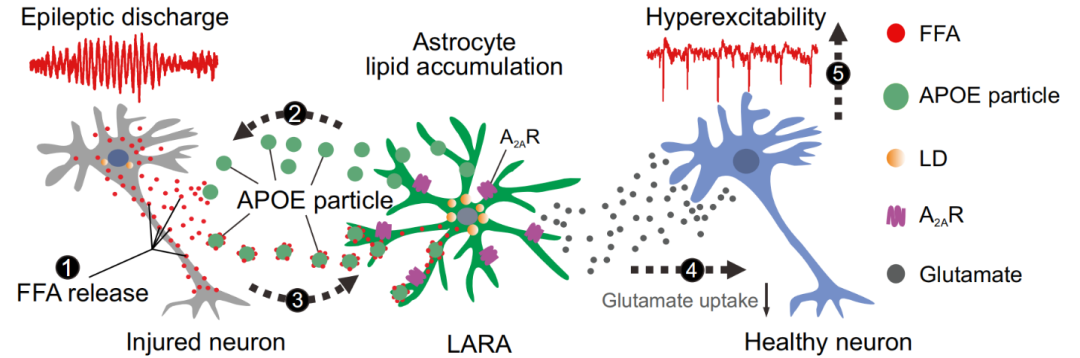
Figure 1. The formation of LARA and the schematic diagram of the principle of promoting the progress of epilepsy
The research results were published in Nature NeurosCience on March 20, 2023 on March 20, 2023 on March 20, 2023. Yan Chao, Liu Xiangyu, and Chen Dijun are the authors of the paper; the Institute of Artificial Intelligence Biomedical Technology of Nanjing University is the communication unit of the paper. The work was supported by projects such as the National Natural Science Foundation.
Original link: https://www.nature.com/articleS/s41593-023-01288-6